Real cracks in real components
Trueflaw produces cracks using a natural thermal fatigue damage mechanism. These cracks are used for flawed specimens in various industries and purposes. In development, flawed samples are used for tuning and testing the developed NDT method with real response. In training, flawed samples are used to give trainees representative feedback to aid learning. In performance demonstration, flawed specimens are used to confirm that the NDT procedure meets the expected performance target. This can mean wide ranging assessment using both theorethical reasoning and test trials (as in ENIQ qualification) or it can mean probability of detection evaluation using, e.g. the ASTM E2862 standard.
Over 8000
That's how many cracks we've manufactured since 2001. Years of research and development ensure you get a quality product.
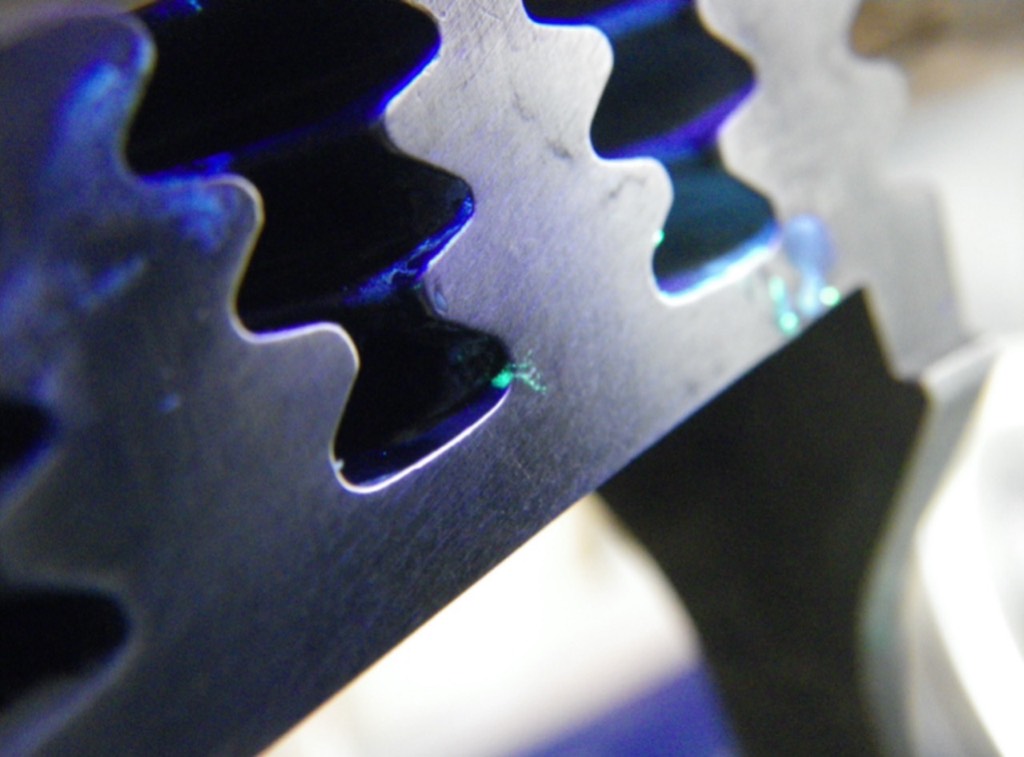

The most representative choice
The produced natural cracks have similar properties to most service induced cracks. There are no changes to the microstructure of the sample or other artifacts induced by the process. Cracks can be produced to various materials and complex shapes. Crack sizes range from 0.3 mm to 100 mm and above. Samples of any size can be handled.
A consistent process
The cracks are produced with an automated industrial process that is highly repeatable. Crack depth information is available through destructive validation of simplified samples. We currently have 10 machines working 24/7 so we can work on several cracks in parallel.
Standard or customized
Trueflaw offers both custom samples tailored to individual tasks and standard samples for process evaluation or POD determination.

eFlaw
In addition to physical flaws, Trueflaw offers eFlaw virtual flaws. They are created by extracting flaw signals from real NDE data. Virtual flaws are an especially interesting new opportunity for mechanized UT inspections.
Virtual flaws for better reliability
Round-robin blind exercises are a good way to measure the capabilities of non-destructive inspections. This is particularly valuable in demanding inspection applications, such as, dissimilar metal weld (DMW) inspection with phased array ultrasonic testing (PAUT) to compare methods and procedures between different parties.
To obtain a proper probability of detection (POD) value of the round-robin attendees, a significant number of cracked samples are required that are often limited. The number of cracks in the data set has been increased by the use of virtual flaws. These flaws are collected from cracked source samples and embedded to new targets, reducing the number of true mock-ups.
In 2022, the second virtual round robin will be organized as a part of international collaboration and is arranged by Aalto University. As before, Trueflaw will contribute virtual flaws to enable testing of realistic data with statistically representative number of laws required to obtain realistic POD.
Extracting and embedding PAUT virtual flaws manually from DMW data is tedious due to the large data size and high number of channels from different angles collected from PAUT inspections. This second round robin employs the next generation of Trueflaw eFlaw virtual flaws. The virtual flaws are extracted with the help of machine learning models, which allows unprecedented precision in flaw extraction and embedding without data artefacts. Improvements in the quality of the flaws on the blind samples results in POD values that better reflect the true detection reliability in these inspections.
We are here to help you.
Please call Kaisa Miettinen (kaisa@trueflaw.com, +358 50 3656862) or Iikka Virkkunen (iikka@trueflaw.com, +358 45 6354415) to discuss more.



